Nanjing Case Study
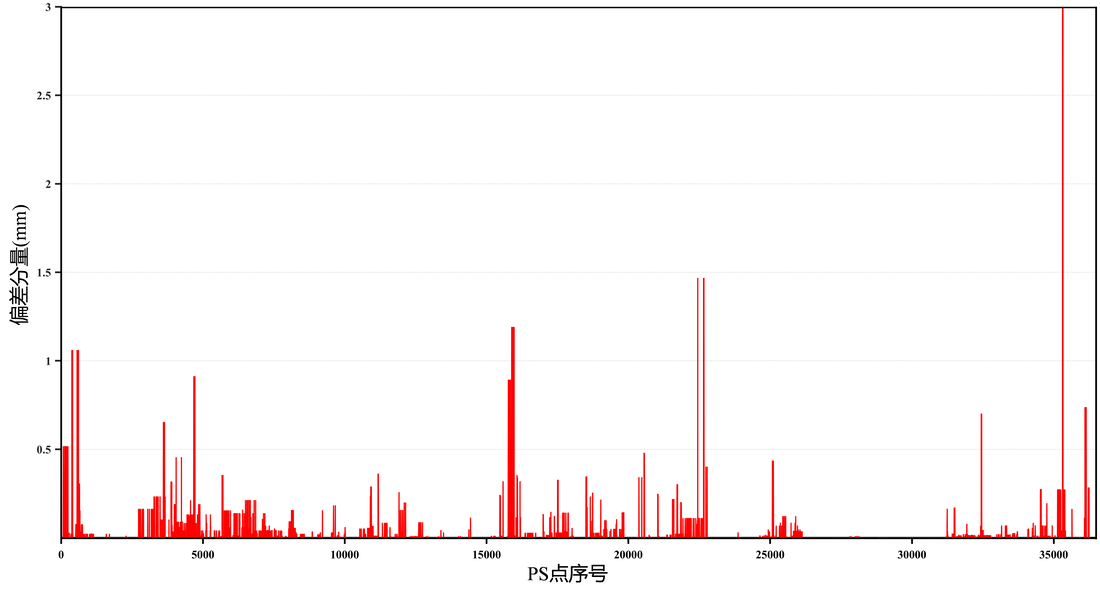
Facing the limitation of the current flow of persistent scatterer SAR interferometry (PSInSAR), we propose a sequential PSInSAR algorithm based on optimized searching-space. The proposed approach achieves a seamless embedding of new SAR images in order to avoid the repeated entire data processing flow of the current PSInSAR tools and achieve a quasi-real-time update of deformation parameters by the induced technical improvement in the differential SAR interferometry (DInSAR) processing and the subsequent deformation time series inversion. Taking the cultural heritage of Nanjing Ming City Wall and its 200-meter buffer zone as an example, we conducted a comparative study of deformation calculation and performance assessment between the current PSInSAR and the sequential PSInSAR method based on the optimized search-space using 32 scenes of Cosmo SkyMed stripmap images (in descending orbits) acquired from January 2015 to February 2018. The results show that the sequential PSInSAR based on the optimized searching-space simplifies the process of DInSAR and achieves a reduced calculation consumption with approximately an order of 10 times by the improved searching mechanism and structure and the resultant reduced calculation complexity of unknown parameters. The cross comparison of deformations from aforementioned approaches indicated a consistent result (the overall dispersion within 0-1 mm), validating the effectiveness and reliability of sequential PSInSAR method proposed. This study reveals the application potential of the sequential PSInSAR approach in the accurate, quasi-real-time deformation monitoring of cultural heritage in the era of remote sensing big data.
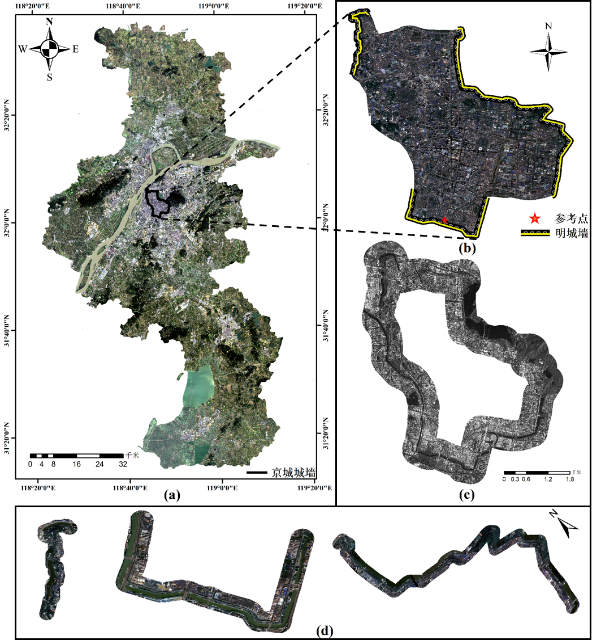
Figure 1 Overview of the study area. (a) The location of Nanjing Ming Dynasty City Walls with the “capital city wall” highlighted by the black polygon, (b) the remains of city wall on the GF-2 imagery, (c) SAR image of "capital city wall" with its region of interest for processing, and (d) three selected sections of heritage walls.
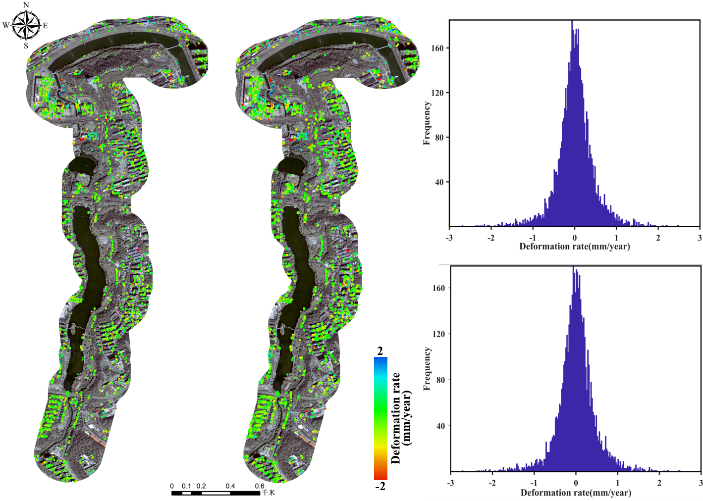
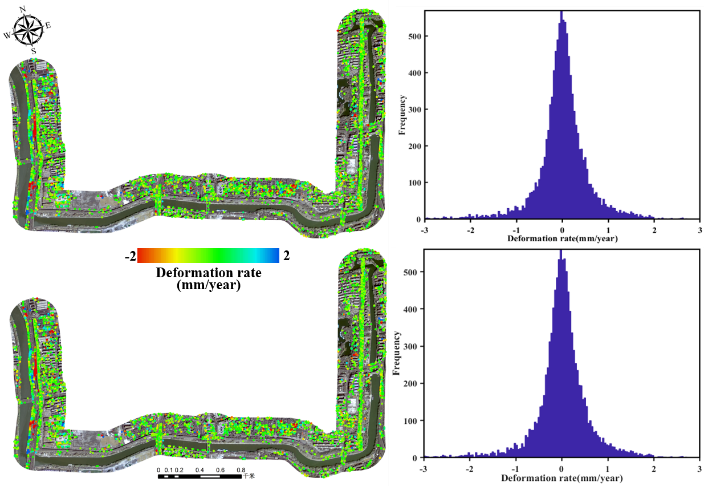
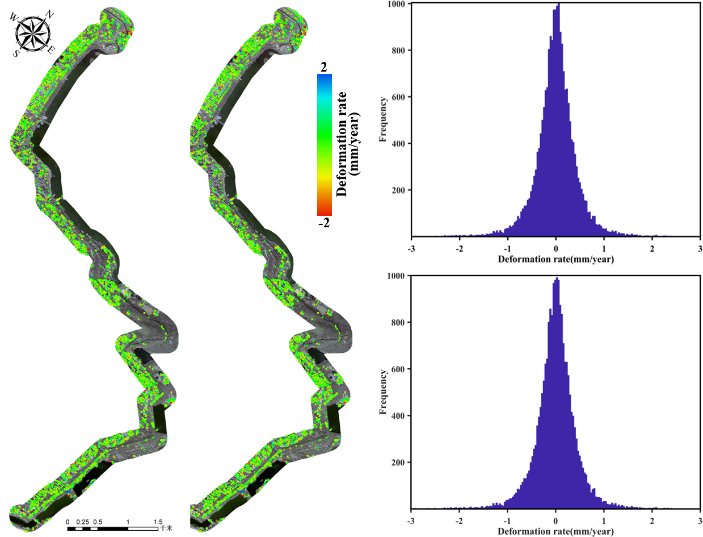
Figure 3 The comparison of the estimated deformations between the PSInSAR and sequential PSInSAR approach along the (a) Shizishan-Dinghuaimen, (b) Xishuiguan-Dongshuiguan and (c) Yueyahu park-Shencemen section of the Nanjing Ming City Wall.